Kinder Pediatric Dental - Bakersfield, CA
Where Smiles Grow & Adventure Reigns
Kinder Pediatric Dental was created with the purpose of providing high-quality dental care that paves the way for kids to build a positive relationship with their smile, now and in the future.


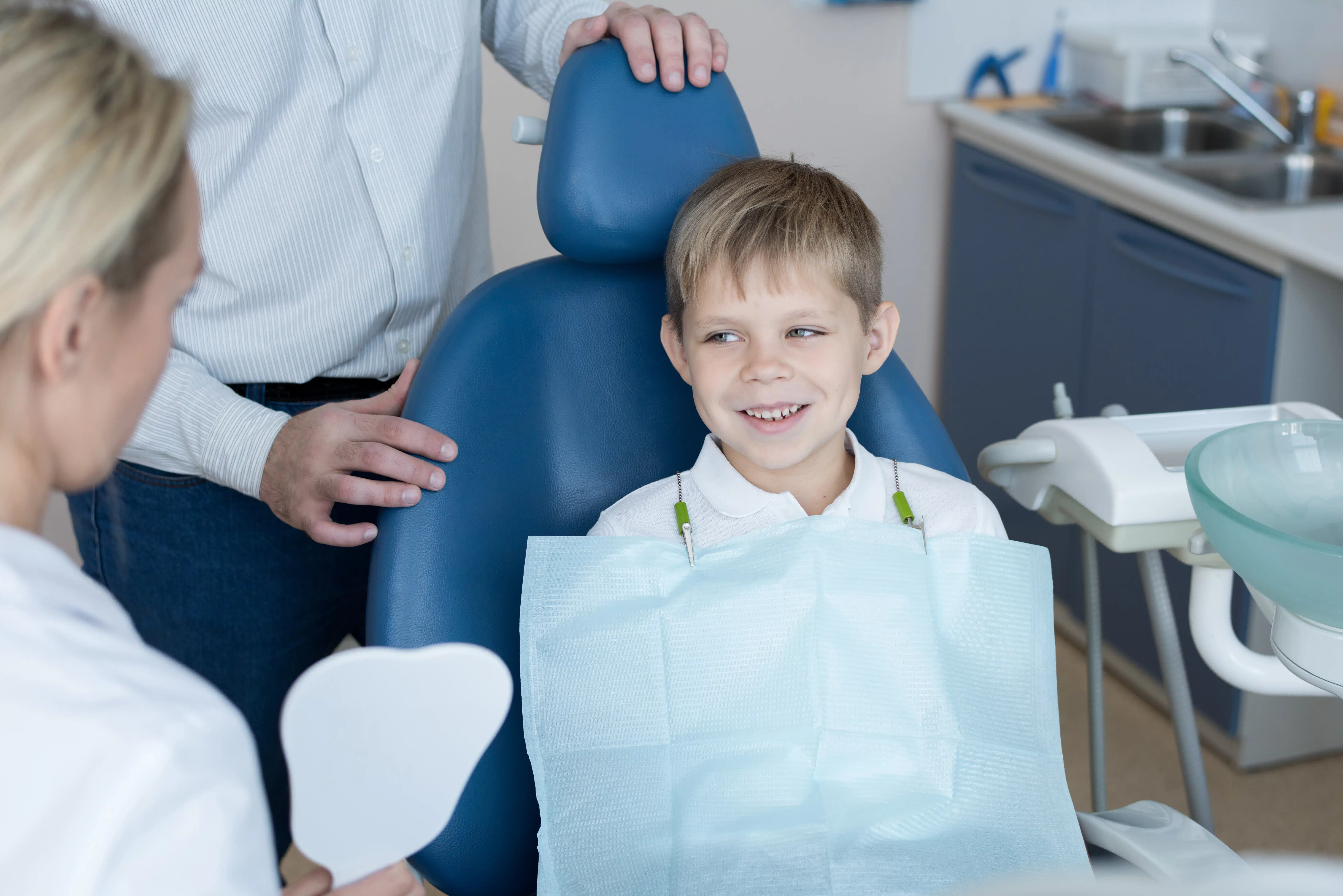
Welcome to Kinder Pediatric Dental!
Bakersfield pediatric dentist
, we focus on more than just teeth. We want to create an environment where kids feel comfortable, safe, and excited about dental care. Through our state-of-the-art Bakersfield, CA facility and highly trained team, we believe that children should lead the dental experience with laughter, fun, and imagination. Only then will we be able to provide the dental care they deserve.- Compassionate Care
- Worry-Free Dentistry
- Patient-Focused
Meet Our Amazing Doctor & Team
Our team is composed of renowned pediatric specialists who are not only experts in their field, but also passionate about providing the best possible care for your child.

Dr. Edward Dove

$99 Cleaning, Exam & X-Ray*
Does your little one need a good dental check-up? Bring them in to Kinder Pediatric Dental, and we’ll take care of everything for just $99! At this price, we will perform a thorough cleaning, examine their smile for any concerns, and take digital x-rays. If we find any problems, we will develop a treatment plan and discuss it with you in detail. We want your little one to enjoy their visit and leave with a healthy, beautiful smile!
*New patients only without insurance.
$69 Emergency Exam & X-Ray
Has your child been complaining of a toothache, sore gum tissue, or any other dental pain? Bring them into Kinder Pediatric Dental for a comprehensive emergency exam and digital x-ray. For just $69, we’ll determine the source of the problem and develop a treatment plan to get your child back to feeling their best.
*New patients only without insurance.

Call Us
Book An Appointment
Visit Us
3130 Union Ave.
Bakersfield, CA 93305
Check Out Our Raving Reviews!
“Excellent service and team! The doctor was very nice and professional. He explained everything very well and answered all my questions.”
Sandra M.

“The team is very kind! My youngest had her first dental procedure there and they did a great job!”
Holly N.

“My kids and I love this doctor. Been going to him for the last 8 years. He is the only dentist I take my kids to. My family and I trust him dearly. Thank you!”
Galaxy W.

Our Services